Getting to Know LoRa Basics™ Station
Exploring the benefits of LoRa Basics™ Station, what it can do and how to use it.
In the How to Use LoRa Basics™ Station technical paper from Semtech, Anton Beitler provides in introduction to LoRa Basics Station including: - What it is - What it can do - How it is built - How it works - Its level of built-in security
The paper begins with an overview of the purpose of a gateway in a LoRaWAN® network, namely, that a gateway is the interface for the LoRaWAN Network Server. It listens to certain parts of the radio spectrum, decodes valid LoRaWAN packets out of LoRa®-modulated signals originating from LoRa-based sensors and forwards them to the network server. He goes on to explain that a gateway can also transmit LoRaWAN packets from the network server down to the LoRa-based sensors as LoRa-modulated signals.
For its part, LoRa Basics Station (Station) is a LoRaWAN gateway software implementation from Semtech which provides core functionality in terms of handling the packet flow, managing spectrum access, network server backhaul connectivity, and more.
LoRa Basics Station handles all tasks related to basic packet forwarding functionality for LoRa-based Class A, B and C end nodes on a LoRaWAN network. In addition, Station has several features that make it particularly advantageous for large-scale gateway deployments for which centralized configuration management and remote inspection capabilities are key. Station’s architecture makes it easy to port to different platforms, even to embedded systems.
Station has been specifically designed with the following aims:
- Ease of portability: The effort of porting Station to a new hardware abstraction layer (HAL) is confined to changes to the radio access layer (RAL) module. The effort of porting Station to a new host platform is confined to changes to the SYS module.
- Ease of testability: Hardware-independent testing can be done by replacing the HAL block with a component which translates the HAL API calls of the RAL with remote procedure calls (RPCs) into the test harness. The LoRa Basics Station regression tests make use of this approach.
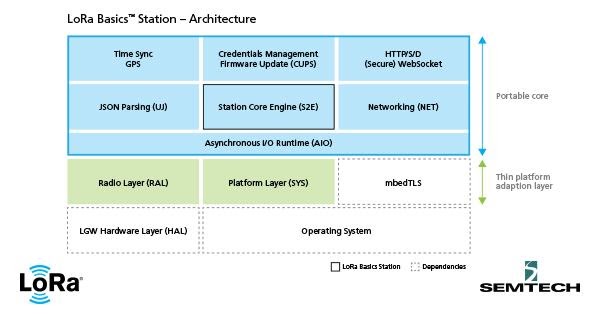
Figure 1: LoRa Basics Station Architecture
As you can see from the block diagram, the RAL, SYS and mbedTLS modules comprise a hardware-specific adaptation layer which provides a unified interface for the system components towards the portable core implementation. At compile-time, the choice for the RAL and SYS layers is made and the resulting object is linked statically with the mbedTLS library.
The portable core is a dependency-free C module built around an asynchronous cooperative multitasking runtime (AIO) and comprises all the core functionality of Station: LoRa packet handling, packet buffering, downlink queue management, spectrum access management, protocol parsing (JSON), protocol state logic, time synchronization, and more.
Not only is LoRa Basics Station both easily portable and easily testable thanks to its resource-efficient lean architecture, but it also sports a host of additional features that make it the clear choice when selecting a gateway implementation for a LoRaWAN network.
Among these features are:
- Support for common Radio Hardware Reference designs
- Full support for Linux hosts
- Secure and firewall-friendly TCP/IP communications
- LoRaWAN Network Server protocol support, including:
- Centralized radio parameter management
- Remote system commands and optional interactive shell
- Flexible health and status reporting mechanisms
- GPS time inference
- Time transfer (facilitating indoor Class B use cases)
- CUPS protocol support, including:
- Transactional updates of connection credentials with roll-back capability
- Secure firmware update delivery with ECDSA signatures
Operating Gateways in practice
LoRa Basics™ Station is becoming the new gateway packet forwarder standard. The protocol is growing in popularity as leading gateway manufacturers are adopting the standard, including Laird, Browan, RAK and Wifx. Due to the many advantages over the UDP packet forwarder, it became the recommended way of connecting gateways to The Things Stack. For enterprise customers, advantages lie in easily managing fleets of gateways and having the ability to remotely update configurations in bulk.
Learn more today about LoRa Basics™Station and The Things Stack:
https://youtu.be/LGFFxPOuSJw
Find documentation about connecting the LoRa Basics Station with The Things Stack in our dedicated website.
Interested in learning more? Read the full paper here.


