Get a standardized report from your LoRaWAN® devices with normalized payloads
The Things Stack introduces payload normalization to standardize sensor data interpretation
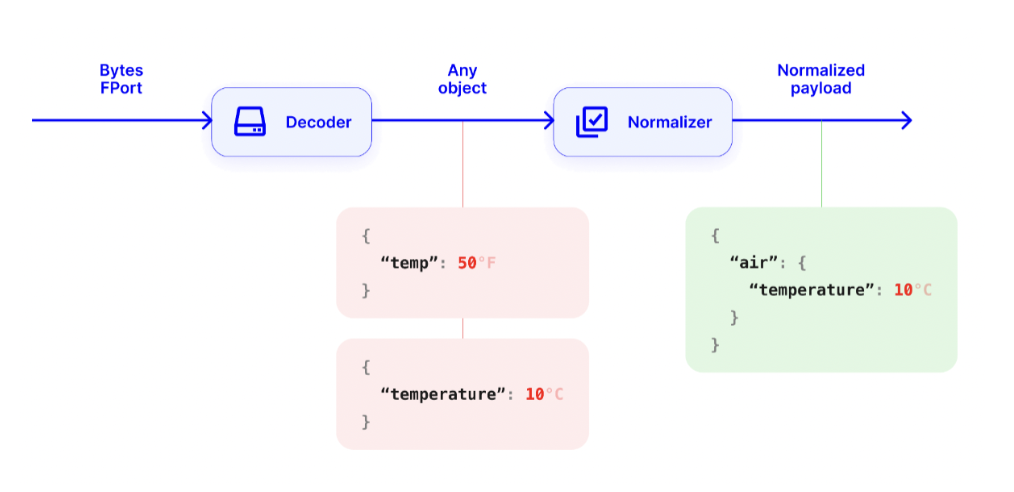
Larger-scale LoRaWAN deployments typically include monitoring different points of data that require a diversity of devices. Interpreting data in such deployments can be difficult due to differences in devices’ payload formats and default decoders especially when different device models monitor the same type of data.
For example, two different temperature sensors report Fahrenheit or Celsius. Their field names can also differ depending on the device's default decoder: as seen in the below example where the field names from two different sensors are “temp” and “ambient_temperature”. Interpreting these readings on the application level becomes a challenge since these differences need to be accounted for. Normalized payload addresses this challenge by defining a standard data structure that is common for all device types.
Learn about the normalized payload schema definition
With a normalized payload, all devices will have the same data format in the applications. This feature is beneficial for:
- Deployments that use devices from various vendors. Payload normalization simplifies application management.
- Integrators. Normalized payloads allow having just one account for interpretation.
Normalized payload decoders can be added to existing devices and coexist with current decoders. This means that the two formats are complementary, allowing data types that are not yet covered by the normalized schema to be decoded in the usual way.
New devices that are going to be released in the market can have the normalized decoder by default.
Learn more about payload normalization. Check out documentation
Start benefiting from the normalized payload and other The Things Stack features. Check out The Things Stack plans